naringin supplier
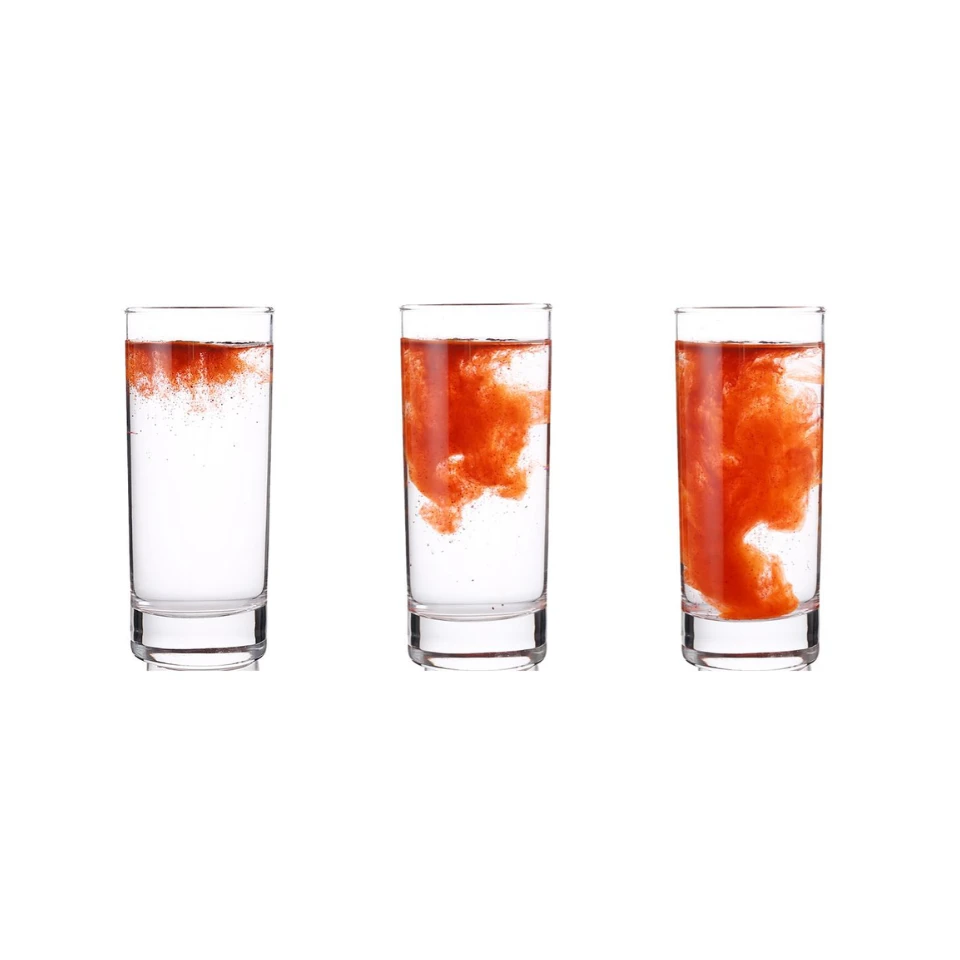
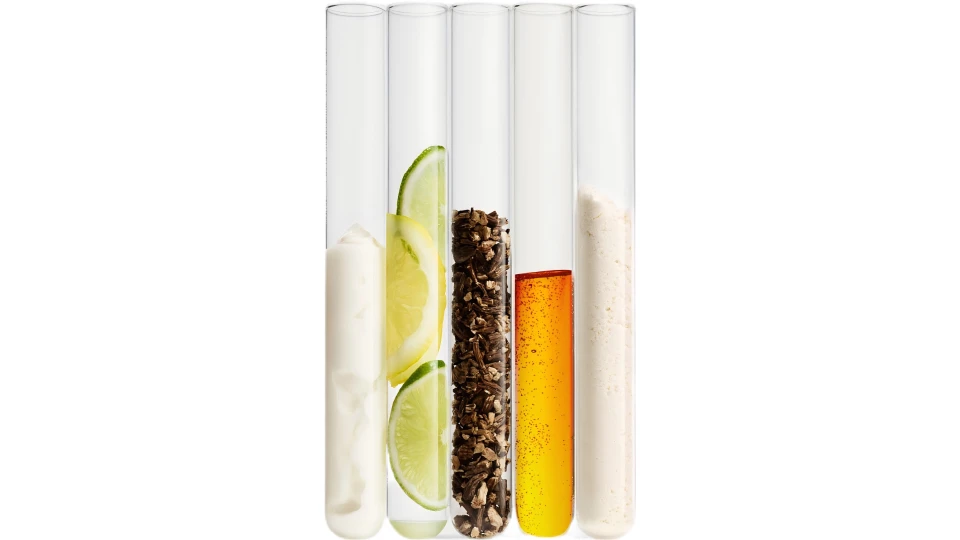
Curcumin 95% for real-world formulators: what’s working now, what still needs work If you’re comparing turmeric extracts this season, Curcumin Turmeric Root Extract Powder Curcuminoids 95% keeps coming up in R&D briefs and supplier calls. To be honest, the category is maturing fast: cleaner spec sheets, tighter color targets, and better water-dispersible grades for beverages. Below is a field-notes style rundown from a practitioner’s perspective—less brochure, more “what we actually see on the bench.” Industry pulse Demand is shifting toward standardized 95% curcuminoids for capsules/tablets and around 10% water-soluble dispersions for ready-to-drink formats. Brands want USP/EP compliance, audited supply chains, and, surprisingly, granular mesh control to reduce dusting on high-speed lines. Many customers say stability in bright, citrusy pH is still the pain point—emulsions help, but taste and ring-staining in PET are recurring themes. Product snapshot and specs Origin: Curcuma longa rhizome; processed at Building 23B1, No.2 Yuanboyuan St., Zhengding Area of China (Hebei) Pilot Free Trade Zone. Offered as 95% curcuminoids granule (20–40 mesh, 40–60 mesh) and ≈10% water-soluble grade. Complies with USP and EP standards. Item Specification Method / Standard Curcuminoids content ≥95% (HPLC); water-soluble grade ≈10% HPLC-DAD; AOAC 2018.16 Mesh size 20–40, 40–60 mesh (granule) Sieve analysis Heavy metals Pb, Cd, As, Hg within USP <232> limits ICP-MS; USP <232> / ICH Q3D Residual solvents Meets USP <467> GC Microbiology TAMC/TYMC, pathogens within USP/EP USP <2021>/<2022> or ISO methods Shelf life 24 months sealed, cool/dry; real-world use may vary Ongoing stability How it’s made (short version) Materials: dried Curcuma longa rhizome. Methods: food-grade solvent extraction, concentration, crystallization/standardization to curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, then granulation to target mesh; water-dispersible grade uses emulsification for better clarity. Testing: HPLC for actives, ICP-MS for metals, GC for solvents, microbiology per pharmacopeia. Service life: typically 24 months; we advise confirmatory stability in your specific matrix and packaging. Where it lands in formulas Nutraceuticals: capsules, tablets, beadlets. F&B: shots, RTD teas, gummies (use water-soluble ≈10%). Cosmetics: color accents in gels/soaps; antioxidant positioning. Functional bakery and dairy analogs (with process-stable dispersions). Advantages we’ve observed: high color strength at 425 nm, consistent flow in 20–40 mesh for tableting, respectable clarity in low-fat beverages (with proper emulsifiers). However, heat/light sensitivity is real—amber packaging and oxygen control help. Vendor comparison (pragmatic view) Vendor Origin Standardization Mesh options Water-soluble Notes Curcumin Turmeric Root Extract Powder Curcuminoids 95% Hebei, China (pilot FTZ) 95% HPLC; USP/EP 20–40, 40–60 ≈10% grade Granule flows well; steady color Generic Trader A Mixed 90–95% Unspecified No/limited Variable lead times Contract Extractor B India 95–98% Custom Yes Higher MOQ, premium Customization, certifications, and data Custom options: mesh tuning, granulation hardness, solvent residue targets, curcuminoid ratio profiling, and packaging (1–25 kg). Certifications available on request typically include GMP, ISO 22000/FSSC 22000, Halal/Kosher. Recent in-house data point: a 95% batch assayed 95.6% total curcuminoids (HPLC), Pb ≤0.5 ppm, As ≤0.3 ppm, residual solvents ND—comfortably within USP/EP guides. Two quick case notes - APAC gummy brand swapped in Curcumin Turmeric Root Extract Powder Curcuminoids 95% water-soluble grade; clarity improved and knife smear dropped ≈15% during pilot, according to their QA. - EU nutraceutical label moved to 40–60 mesh granules; line dusting reduced noticeably (operator feedback), with same HPLC potency after 6-month ICH zone storage. Final thought: curcumin still rewards disciplined formulation—antioxidant systems, light protection, and a bit of patience during dispersion. But when the spec is right, it behaves. References EFSA Panel on Food Additives. Re-evaluation of curcumin (E 100). EFSA Journal. https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1679 JECFA. Curcumin monograph and ADI. WHO/FAO Food Additives. https://www.who.int/foodsafety/areas_work/chemical-risks/jecfa AOAC Official Method 2018.16: Curcuminoids in Turmeric by HPLC-DAD. https://www.aoac.org/official-methods-of-analysis USP General Chapters <232> (Elemental Impurities) and <467> (Residual Solvents). https://www.uspnf.com
Finutra devotes to be an integrated supplier for global supply chain, we offer a
broad array of raw materials and functional ingredients
Authoritative Certification
Continuous Innovation, Customer First
Enhance core competitiveness to bring customers better products and services,
Each of these is the result of our team's relentless pursuit of excellence
and our deep commitment to social responsibility.








Global
Reach
FINUTRA has over 350,000 square feet of manufacturing and warehouse
space worldwide.
Industries We Serve
Advanced molecular distillation and microencapsulation
technology. Extremely bioavailable
trace carotenoids Intuitively soluble.


STAY UPDATED
Receive special offers and first look at new
products.
products.
Building 23B1, No.2 Yuanboyuan St., Zhengding Area of China (Hebei) Pilot Free Trade Zone
QUICK LINK
Finutra devotes to be an integrated supplier for global supply chain, we offer a broad array of raw
materials and functional ingredients as a manufacturer, distributor and supplier for global Beverage,
Nutraceutical, Food, Feed and Cosmeceutical.
Copyright © 2025 Hebei Finutra
Biotech Co.,
Ltd. All
Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy